How Thyroid Hormones are Made
Jun 6, 2019
Thyroid Hormone Metabolism
Thyroid hormone is indispensable for normal development and metabolism of most cells and tissues. Thyroid hormones are metabolized by different pathways: glucuronidation, sulfation, and deiodination, the latter being the most important. Thyroid hormones are created by adding or removing iodine molecules from chemicals produced within the thyroid gland.
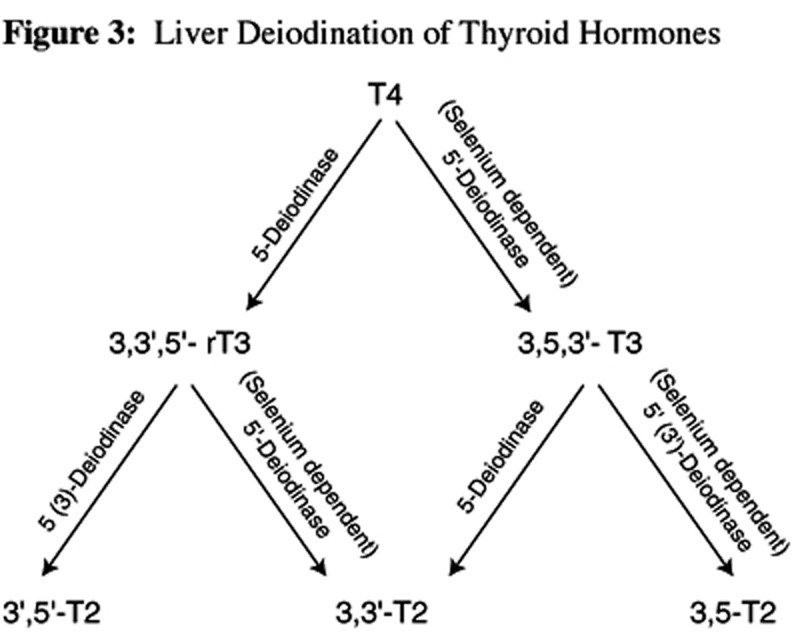
Iodine is an important nutritional element that the thyroid stores and uses to create its primary hormone Thyroxine (T4). A protein within the thyroid gland called thyroglobulin reacts with the stored iodine to create precursors used to produce thyroid hormones. These precursor products are called iodotyrosines and include monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine. Triiodothyronine is formed when diiodotyrosine is combined with monoiodotyrosine within in the colloid of the thyroid follicle (follicles are located within the thyroid gland). Two molecules of diiodotyrosine combine to make the thyroid hormone thyroxine. Remember, roughly 20% of the daily triiodothyronine supply is secreted by the thyroid after being synthesized through this process. The other 80% is produced from thyroxine within peripheral tissues through a process called deiodination, or the removal of iodine, from a specific location on the molecule. Only a small amount of T3 is secreted directly from the thyroid compared to thyroxine, which is the primary hormone produced and released. Therefore, the process of deiodination is critical for achieving adequate levels of T3. Patients who have disruption of this process may continue to experience symptoms of hypothyroidism while taking levothyroxine monotherapy since they are unable to convert the T4 into T3.
Deiodination: Necessary for healthy thyroid hormone balance
Deiodination is the process by which an iodine molecule is removed from Iodotyrosines that makeup thyroxin, basically reversing the iodination process that created it. Deiodination converts T4 into equal amounts of T3 and reverse T3, depending on the location where the iodine was removed. Deiodination occurs again down the pathway to release iodine from Iodotyrosines that make up T3 and rT3, converting a % of each hormone into a metabolite known as 3,5-diiodothyronine (T2). The process of deiodination, or the release of iodine, is an important aspect of thyroid hormone metabolism and the synthesis of physiologically active hormones, including T3.
References for the above paragraph: References for the above paragraph:
- Metabolism of Thyroid Hormone Robin P Peeters, M.D. Ph.D. and Theo J Visser, Ph.D.
- Thyroid Gland, Anatomy, and Physiology Wilmar M. Wiersinga, in Encyclopedia of Endocrine Diseases, 2004